NAME
App::GUI::Harmonograph - sculpting beautiful circular drawings
SYNOPSIS
read this POD or check dialogs from help menu
start the program (
harmonograph)move knobs and observe how preview sketch reacts til you got an interesting configuration
push Draw (right below drawing board or
Ctrl+DorAlt+D) to produce full imagechoose Save in Image menu (or
Ctrl+S) to store image in a PNG / JPEG / SVG filechoose Write in settings menu (
Ctrl+W) to save settings into an INI file for tweaking them later
Please note that quick preview gets not triggered by GUI elements in the PEN SETTINGS section (last tab).
After first use of the program, a config file will be created under ~/.config/harmonograph in your home directory. It contains mainly stored colors and dirs where to load and store setting files. You may change it manually or deleted it to reset defaults.
DESCRIPTION
An Harmonograph is an apparatus with several connected pendula, creating together spiraling pictures :
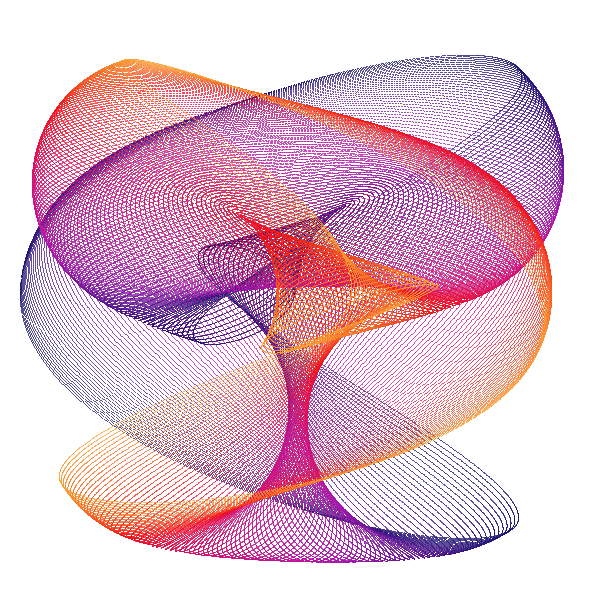
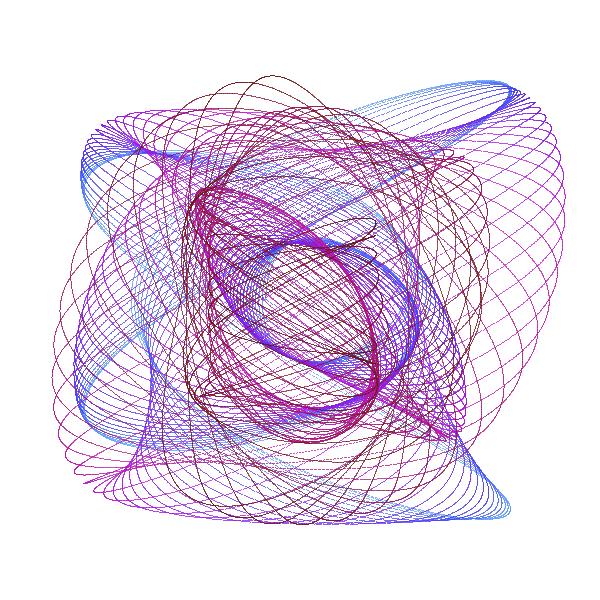
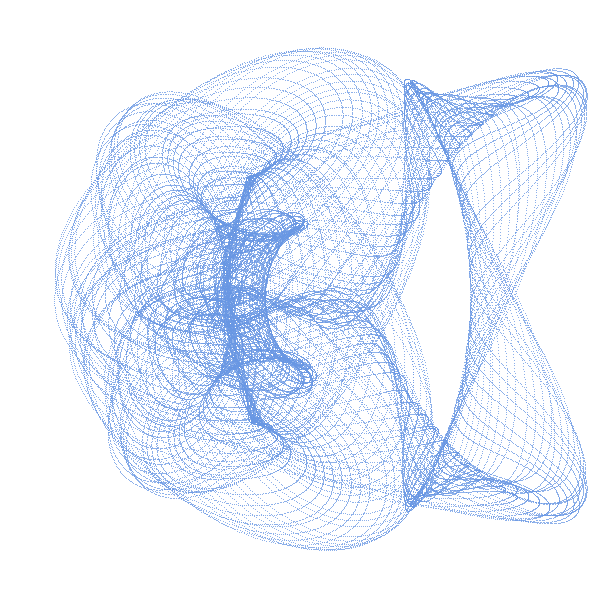
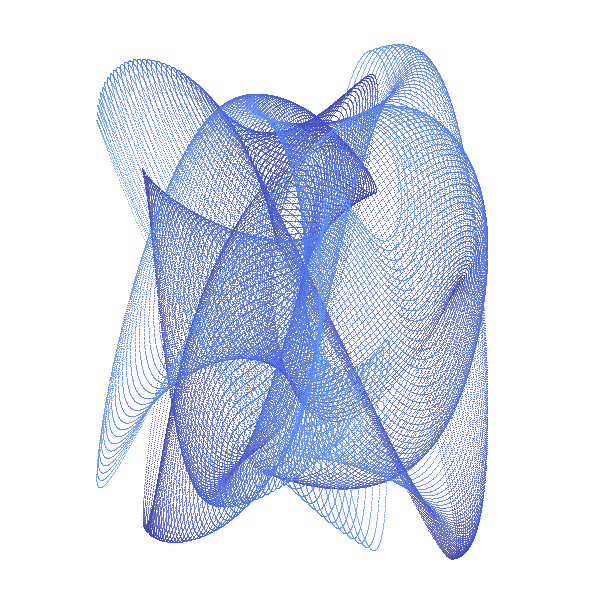
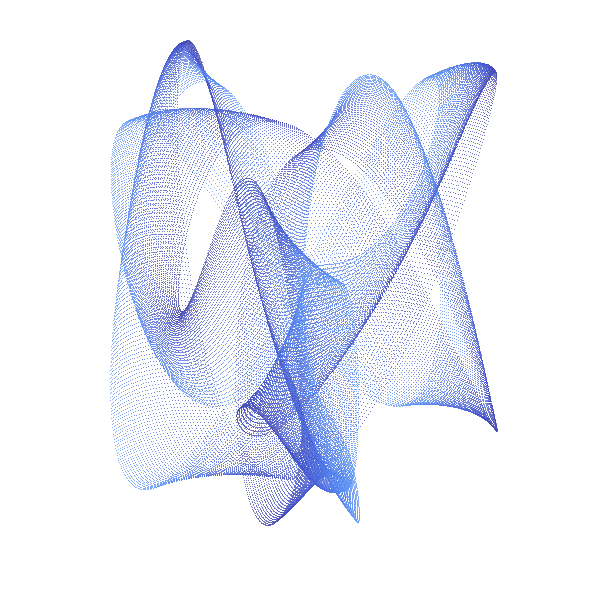
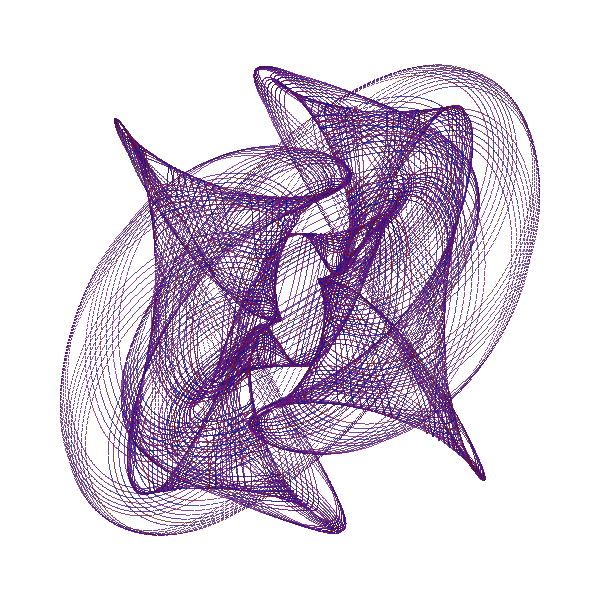
This is a cybernetic recreation of an Prof. Blackburns invention with several enhancements:
third pendulum can rotate
pendula can oscillate at none integer frequencies
separate complex amplitude and frequency damping
draw lines or dots with changeable density and size
3 types of color changes with changeable speed and polynomial dynamics
Mechanics
The classic Harmonograph is sturdy metal rack which does not move while 3 pendula swing independently. Let us call the first pendulum X, because it only moves along the x-axis (left to right and back). In the same fashion the second (Y) only moves up and down. When both are connected to a pen, we get a combination of both movements. As long as X and Y swing at the same speed, the result is a diagonal line. Because when X goes right Y goes up and vice versa. But if we start one pendulum at the center and the other at the upmost position we get a circle. In other words: we added an offset of 90 degrees to Y (or X). Our third pendulum Z moves the paper and does exactly the already described circular movement without rotating around its center. If both circular movements (of X, Y and Z) are concurrent - the pen just stays at one point over the paper, If both are countercurrent - we get a circle. Interesting things start to happen, if we alter the speed of of X, Y and Z. Than famous harmonic pattern appear. And for even more complex drawings I added R, which is not really a pendulum, but an additional rotary movement of Z around its center. The pendula out of metal do of course fizzle out over time, which you can see in the drawing, in a spiraling movement toward the center. We emulate this with two damping factors: one for amplitude and one for the frequency (speed).
GUI
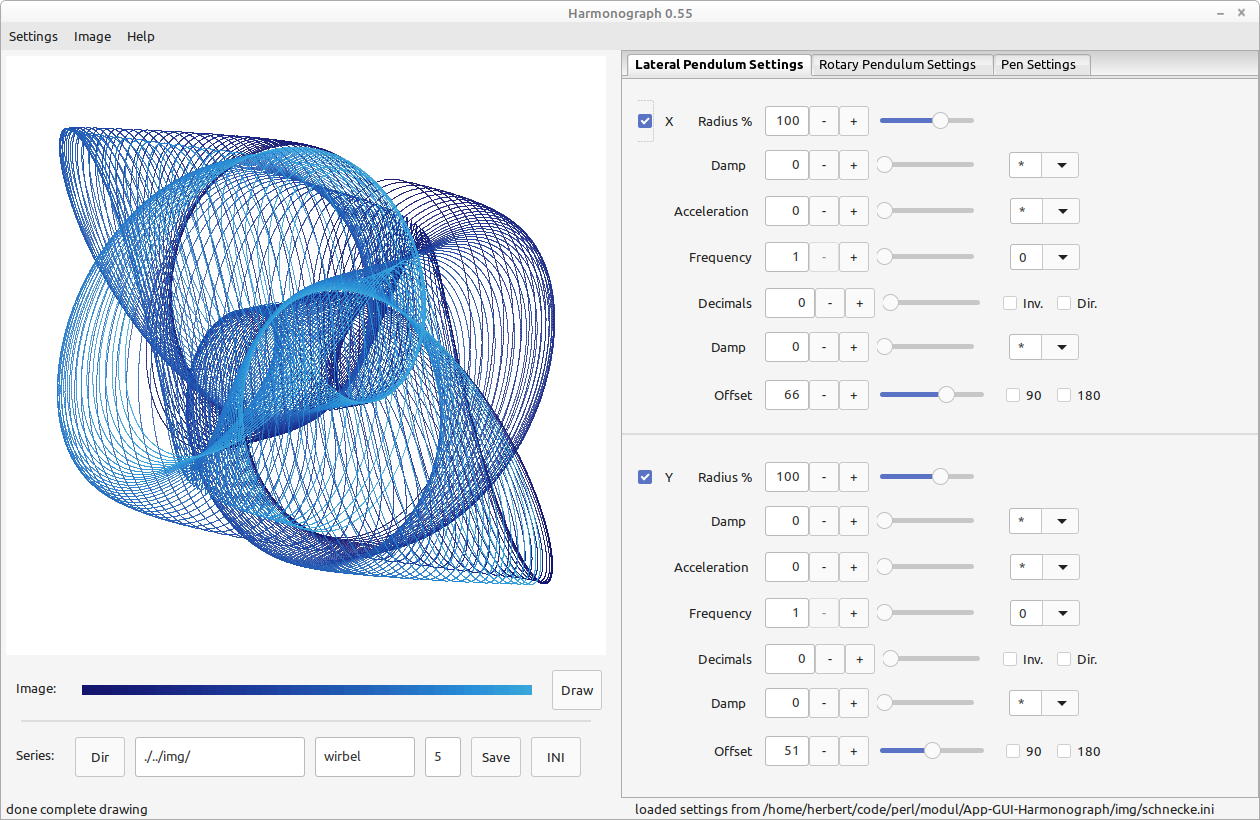
The general layout of the program has three parts, which flow from the position of the drawing board.
In the left upper corner is the drawing board - showing the result of the Harmonograph.
The whole right half of the window contains the settings, which guide the drawing operation. These are divided into four tabs - roughly devided in form (3) and decoration (last one).
The lower left side contains buttons which trigger a few commands, mostly for mass productions of image files. All the other commands are only reachable in the main menu or by keyboard (key combinations are displayed in the menu).
Please mind the tool tips - short help texts which appear if the mouse stands still over a button or slider. Also helpful are messages in the status bar at the bottom - on bottom left regarding images and bottom right about settings. When brwosing the main menu, help texts about the highlighted item also appears in the status bar. The Menu can be completely navigated with the keyboard. Just hold Alt and use the direction keys (up, down, left and right) or the highlighted letters. When holding the Alt key you can also see which Alt + letter combinations trigger which button.
Pendulum
Each of the first two tabs contains the settings of two pendula. The first tab has the lateral pendula: X (left right movement) and Y (up and down). The second tab has Z (wobble - moving the center of the paper in rotating movement around the center of the space without rotating the paper) and R (actual rotation around center of the pater). Most settings can be changed with a combo-slider which allows input by typing, moving the slider or fine tuning the value by pushing the minus and plus buttons. The settings for each pendulum are identical and are as follow:
Each pendulum section starts with the name of the pendulum, but in front of that (tothe right) is a checkbox to (de-)activate the entire pendulum. The first row lets you dial in the speed (frequency). This is most fundamental to the shape of the drawing. For instance 2 means that the pendulum swings back and fourth twice as fast. To the right you can choose an additional factor the frequency gets multiplied with. This can be a constant like Pi or Phi or the frequency of another pendulum or just simply one. This is especially handy when browsing the classic shapes with three pendula. For these the frequency of X and Y has to be the same - which will be ensured when you set the frequency factor of Y to X (or vice versa) and keep the frequency of the connected pendulum to one. The next combo control below adds decimals to the frequency value for more complex rotating drawings. Behind that are two check boxes to invert the final frequency value to 1/x or to flip the direction of the pendulum. Below that follows a frequency damping, which will change the frequency over time. To the right of that value you can set the damping mode. Set it to minus for linear damping or to "*" for accelerated damping. the same as the second row only with slightly different optical results.
The fourth row starts with a slider to fine tune the starting point of the pendulum. It can be chosen between zero and a quater rotation. This can have great effects on the shape. Because of the special desirability offsets of an half (180 degree) or quarter (90 degree) rotation can be activated by checkbox (to the right of the slider). The final offset is the sum of the checked with the slider value.
The fifth row is the amplitude size, which simple allows to make the picture larger or smaller depending if the pendulum left the frame or doesn't move enough. As with reqency, also the amplitude can be damped over time and this damping can accelerated.
Mod Matrix
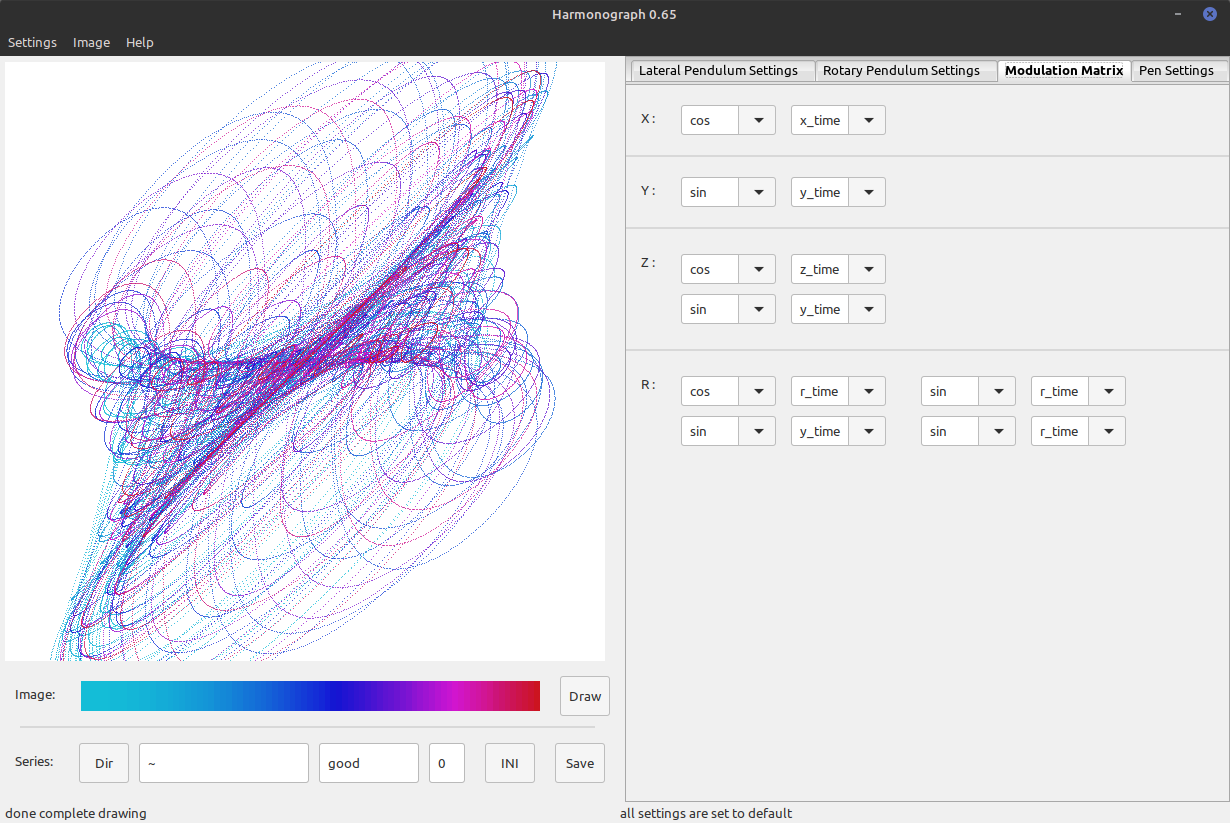
The third tab allows the deepest alterations to the drawing, which leaves the original concept of a Harmonograph. For instance the X - Pendulum is basically a little more than the a cosine function to the time variable. The time variable represents the frequency since we simulate a double frequency by doubling the speed time passes for this pendulum. If you change the function from cosine (cos) to tangent or other trigonometric functions the shapes will change redically. Same goes for Y and Z which is computation wise just a combination of X and Y applied to a offset. R is different since its computed with a rotation matrix. But in same manner as X or Y you can change here for each cell of the matrix the variable and the function that computes on that variable. Please note the most beautiful examples were computed by changing the variable of just one cell of the rotation matrix.
Pen Settings
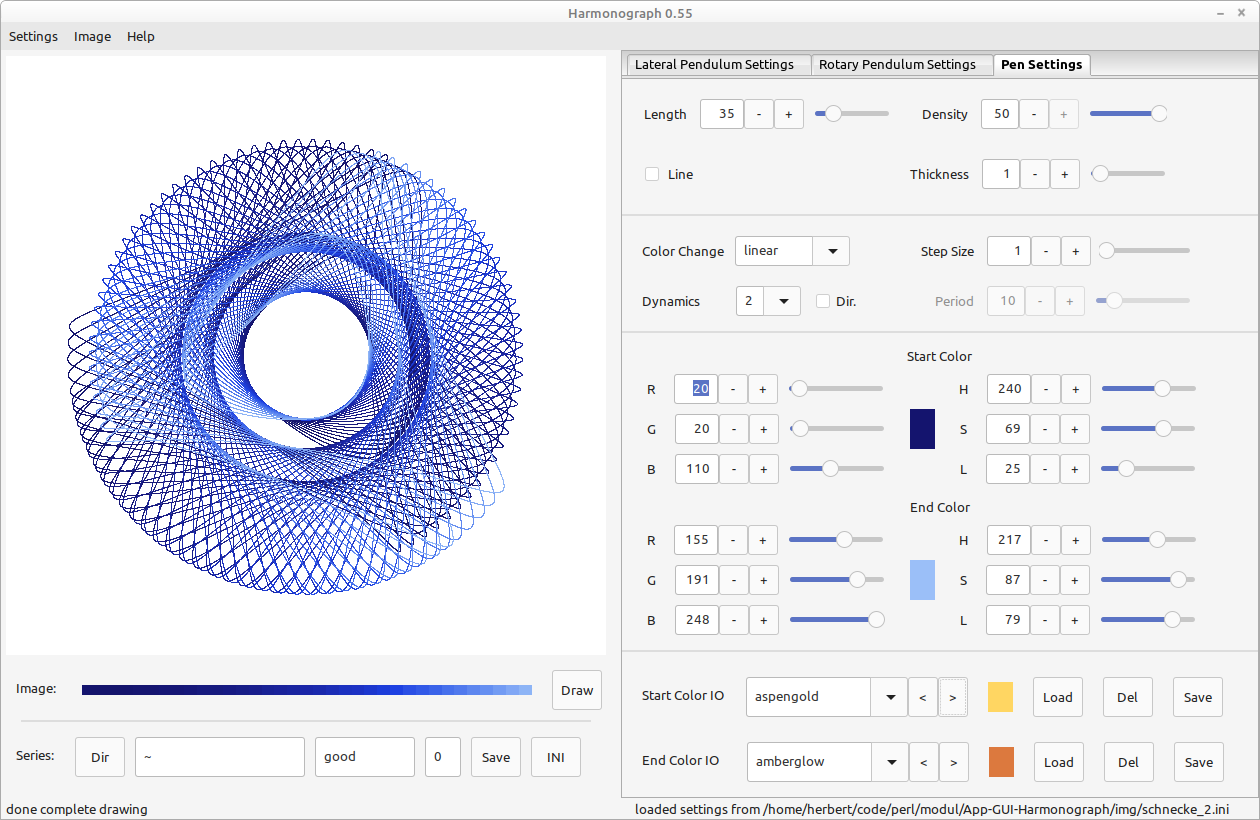
The last tab on the right contains the visual properties (of the pen). In left upper corner yo set the amount of rotations (swings) to be drawn. Right beside is the distance between dots. Greater distances, together with color changes, help to clearify muddled up drawings. Also - many rotations and little distance between dots will slow down the computation. In the second row left is a checkbox to answer if the dots should be connected. The fourth selector sets the dot size in pixel. Zero mens here very thin = one half of an pixel - which is still visible, but very airy.
Colors
On the lower part of the pen settings tab are the are the options for colorization and this has in itself three parts. Topmost are the settings for the color change, which is set on default to no. In that case only the upper start color (below the color change section) will be used, and not the end color (target - which is even below that).
Both colors can be changed via controls for the red, green and blue value (see labels "R", "G" and "B" ) or hue, saturation and lightness (HSL). The result can be seen in the color monitor at the center of a color browser.
An one time or alternating gradient between both colors with different dynamics (first in second row) can be employed. Circular gradients travel around the rainbow through a complement color with saturation and lightness of the target settings. Steps size refers always to how maby circles are draw before the color changes.
The third part of the tab grants you access to the color section of the config file .harmonograph. There you can store your favorite colors under a name and reload or delete them later. The upper row is for interactions with the start color and the lower with the end color.
Commands
In the lower left corner are two rows of command buttons. All other commands are in the menu.
The upper row has only one button for making a full drawing. This might take some time if line length and dot density are high. For that reason - only changes on the pendulum settings (first two tabs) produce an sketch drawing, helping the user understand the nature his changes. A sketch contains only the first five pendulum swings, so it can be drawn fast enough for almost immediate interactions. For a full drawing that takes all settings into account you need to push Draw button or Press Ctrl + D.
The second row has commands to quickly save many files. First push Dir to select the directory and then type directly into the second text field the file base name. The index in the next one is found automatically. Every time you now press Save a file with the current image is saved under the path: dir + base name + index + ending (set in Menu: Image > Format and saved in configs). The index automatically autoincrements when producing a file. Push button INI next to it to also save the settings of the current state under same file name, but with the ending .ini.
Menu
The upmost menu bar has only three very simple menus. Please not that each menu shows which key combination triggers the same command and while hovering over an menu item you see a short help text the left status bar field.
The first menu is for loading and storing setting files with arbitrary names. I recommend giving them the file ending .ini for transparency reasons. A submenu allows a quick load of the recently used files. The first entry lets you reset the whole program to the starting state and the last is just to exit (safely with saving the configs).
The second menu has only two commands for drawing an complete image and saving it in an arbitrary named PNG, JPG or SVG file (the file ending decides). The submenu above only sets the preferred format, which is the format of the serially save images by the command buttons in the left lower corner. The preferred file format is also the first wild card in the save dialog. Above that is another submenu for setting the image size.
The third menu has some dialogs with documentation and additional information.
SEE ALSO
AUTHOR
Herbert Breunung (lichtkind@cpan.org)
COPYRIGHT & LICENSE
Copyright(c) 2022-23 by Herbert Breunung
All rights reserved. This program is free software and can be used, changed and distributed under the GPL 3 licence.