NAME
Number::RangeTracker - Keep track of numerical ranges quickly
VERSION
Version 0.6.1
SYNOPSIS
Create and modify ranges (three range syntaxes shown):
my $range = Number::RangeTracker->new;
$range->add( [ 1, 10 ], '11..20' );
$range->remove( 6, 15 );Output ranges, their complement, or integers within ranges (differences between scalar and list contexts shown):
$range->output;
# Scalar context: '1..5,16..20'
# List context: ( 1 => 5, 16 => 20 )
$range->complement;
# Scalar context: '-inf..0,6..15,21..+inf'
# List context: ( -inf => 0, 6 => 15, 21 => +inf )
$range->integers;
# Scalar context: '1,2,3,4,5,16,17,18,19,20'
# List context: ( 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20 )Examine range characteristics:
$range->length; # 8
$range->size; # 10
$range->is_in_range(100); # 0
$range->is_in_range(18); # 1, 16, 20DESCRIPTION
An instance of the Number::RangeTracker class is used to keep track of a set of numerical ranges. Ranges can be added to and removed from this collection of ranges. Overlapping ranges are collapsed to form a single, longer range. Ranges can be manipulated, examined, and output in a variety of ways.
While some other modules associate values with a range of keys (see "SEE ALSO"), the objective of Number::RangeTracker is to quickly and easily monitor the integers on a number line that are covered by at least one range. Number::RangeTracker performs significantly faster than other modules that have similar functions (see "SEE ALSO").
- new
-
Initializes a new Number::RangeTracker object.
- add( START, END )
-
Add one or more ranges. This can be used multiple times to add ranges to the object. Ranges can be added in several ways. The following are equivalent.
$range->add( [ 1, 10 ], [ 16, 20 ] ); $range->add( 1, 10, 16, 20 ); $range->add( '1..10', '16..20' ); - remove( START, END )
-
Remove one or more ranges from the current set of ranges. This can be used multiple times to remove ranges from the object. Ranges can be removed with the same syntax used for adding ranges.
- collapse
-
When ranges are added or removed, overlapping ranges are not collapsed until necessary. This allows range Number::RangeTracker to be very fast.
Ranges can be manually collapsed to avoid memory issues when working with very large amounts of ranges. In one test, a million overlapping ranges required ~100 MB of memory. This requirement was cut drastically by collapsing ranges after every 100,000th range was added.
Ranges are automatically collapsed (and merged or removed where appropriate) (1) before ranges are added (if there are ranges still waiting to be removed) and (2) before each of the following methods is executed.
- length
-
Returns the total length of all ranges combined.
- size
-
Returns the total number of elements (i.e., integers) of all ranges.
- is_in_range( VALUE )
-
Test whether a VALUE is contained within one of the ranges. Returns 0 for a negative result. Returns a list of three numbers for a positive result: 1, start position of the containing range, end position of the containing range.
- output
-
Returns all ranges sorted by their start positions. In list context, returns a list of all ranges sorted by start positions. This is suitable for populating a hash, an array, or even another range object. In scalar context, returns a string of ranges formatted as:
1..10,16..20. - integers
-
Returns each integer contained within the ranges. In list context, returns a sorted list. In scalar context, returns a sorted, comma-delimited string of integers.
- complement( UNIVERSE_START, UNIVERSE_END )
-
Returns the complement of a set of ranges. The output is in list context sorted by range start positions.
my $original_range = Number::RangeTracker->new; $original_range->add( [ 11, 20 ], [ 41, 60 ], [ 91, 110 ] ); my %complement = $original_range->complement; # -inf => 10, # 21 => 40, # 61 => 90, # 111 => +infUNIVERSE_START and UNIVERSE_END can be used to specify a finite subset of the 'universe' of numbers (defaults are -/+ infinity. The complement ranges are bounded by these values.
%complement = $original_range->complement( 1, 50 ); # 1 => 10, # 21 => 40A new object with the complement of a set of ranges can be created quickly and easily.
my $complement_range = Number::RangeTracker->new; $complement_range->add( $original_range->complement );
SEE ALSO
- Monitor the integers covered by at least one range
-
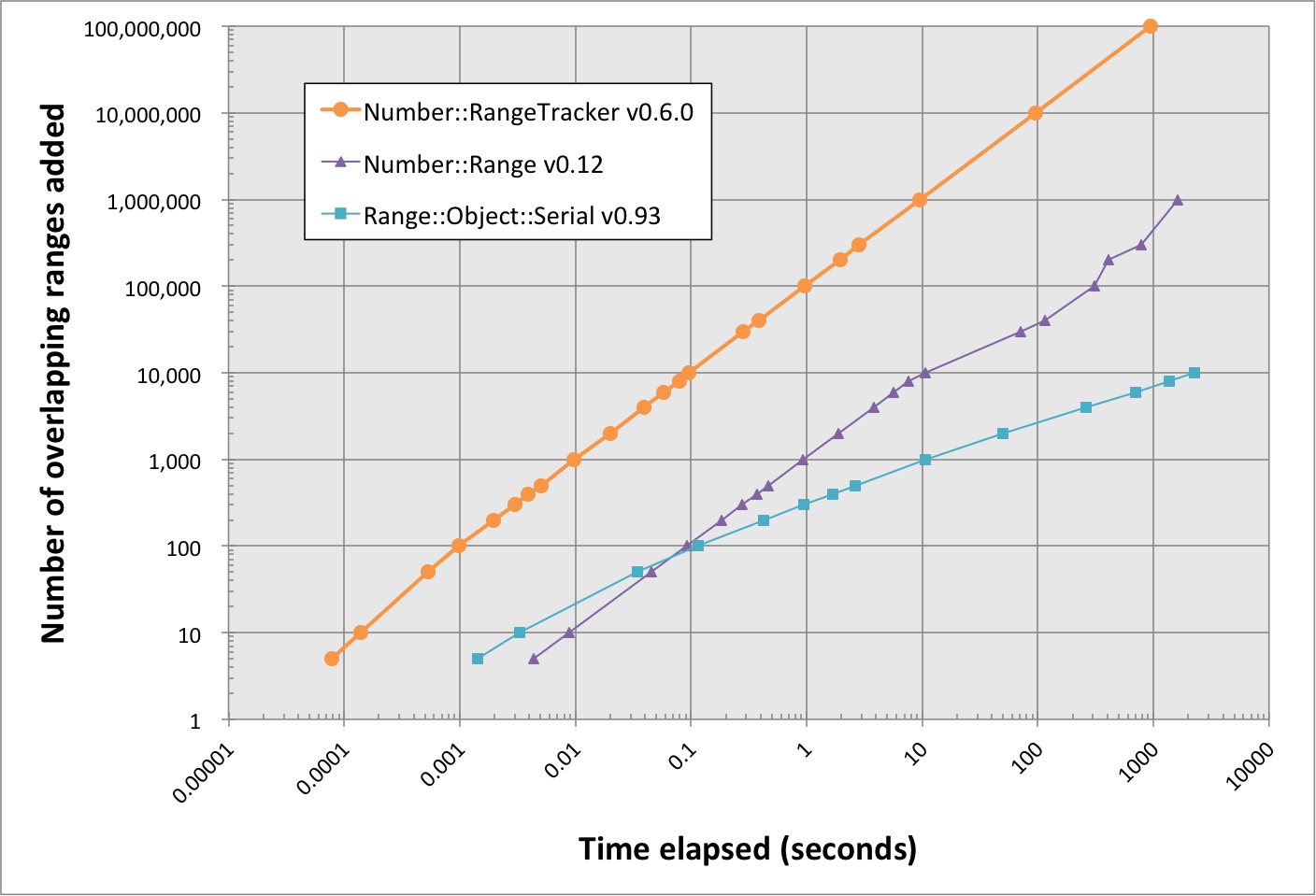
Although there is some functional overlap between this module, Number::Range, and Range::Object::Serial, Number::RangeTracker is significantly faster.
It takes less than one second for Number::RangeTracker to add 100,000 overlapping ranges. Over this same period of time, Number::Range and Range::Serial::Object are only able to add 1,000 and 300 ranges, respectively.
Some tasks require even higher throughput. When adding 1 million overlapping ranges, Number::Range took >250 times as long as Number::RangeTracker (35 min 31 sec vs. 8 sec). Range::Object::Serial slows exponentially as ranges are added and, therefore, it was not feasible to test this many ranges.
- Ranges with strandedness (like double-stranded DNA or mile posts on a two-way road)
- Compare numbers in an imprecision-tolerant manner
- Named ranges
SOURCE AVAILABILITY
The source code is on Github: https://github.com/mfcovington/Number-RangeTracker
AUTHOR
Michael F. Covington, <mfcovington@gmail.com>
BUGS
Please report any bugs or feature requests at https://github.com/mfcovington/Number-RangeTracker/issues.
INSTALLATION
To install this module from GitHub using cpanm:
cpanm git@github.com:mfcovington/Number-RangeTracker.gitAlternatively, download and run the following commands:
perl Build.PL
./Build
./Build test
./Build installSUPPORT AND DOCUMENTATION
You can find documentation for this module with the perldoc command.
perldoc Number::RangeTrackerLICENSE AND COPYRIGHT
Copyright 2014 Michael F. Covington.
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the the Artistic License (2.0). You may obtain a copy of the full license at:
http://www.perlfoundation.org/artistic_license_2_0
Any use, modification, and distribution of the Standard or Modified Versions is governed by this Artistic License. By using, modifying or distributing the Package, you accept this license. Do not use, modify, or distribute the Package, if you do not accept this license.
If your Modified Version has been derived from a Modified Version made by someone other than you, you are nevertheless required to ensure that your Modified Version complies with the requirements of this license.
This license does not grant you the right to use any trademark, service mark, tradename, or logo of the Copyright Holder.
This license includes the non-exclusive, worldwide, free-of-charge patent license to make, have made, use, offer to sell, sell, import and otherwise transfer the Package with respect to any patent claims licensable by the Copyright Holder that are necessarily infringed by the Package. If you institute patent litigation (including a cross-claim or counterclaim) against any party alleging that the Package constitutes direct or contributory patent infringement, then this Artistic License to you shall terminate on the date that such litigation is filed.
Disclaimer of Warranty: THE PACKAGE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS' AND WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES. THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT ARE DISCLAIMED TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY YOUR LOCAL LAW. UNLESS REQUIRED BY LAW, NO COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTOR WILL BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THE PACKAGE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.